What Is VoIP? A Comprehensive Guide to How Business VoIP Works
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is one of those technologies that you use more often than you realize, even though you may never have heard the term before. Skype, Xbox Live, Ventrilo, Discord, Apple FaceTime—if you’re familiar with any of these, then you’re already familiar with VoIP. So what is it?
In short, VoIP is digital calling over the Internet. It’s even right in the name: Voice over IP. As the Internet developed and various protocols were introduced, multiple innovators realized they could use the new technology to send voice signals for free rather than relying entirely on landlines. Because VoIP uses packet switching instead of circuit switching like landlines (think switchboards and operators), the cost associated with traditional telephone companies is all but wiped out.

VOIP text on abstract phone screen hanging from a chain. 3D rendering
A Brief History of VoIP
Internet calling has a longer life span than you might think. It roughly started in 1973 when ARPANET experimented with the first VoIP transmissions. Another big breakthrough came in 1991 with Speak Freely, the first VoIP app released into the public domain. It wasn’t until 1995, however, that the first real for-profit VoIP application came into play. Israeli telecom company VocalTec released their InternetPhone, and while it charged users for registration and minutes, the cost was minuscule compared to average call pricing at the time. Hosted PBX and SIP followed the next year, and then in 2003 came the biggest VoIP release in terms of public perception: Skype.
For any non-gamers (Xbox Live, which also uses VoIP, launched in 2002), free Internet calling was a phenomenon. Interest skyrocketed to the point that the FCC got involved in 2004. They declared VoIP an information service, not a telephone service. This meant that VoIP providers were not beholden to the higher taxes of telecom giants and were also free from state regulation, keeping VoIP costs incredibly low.
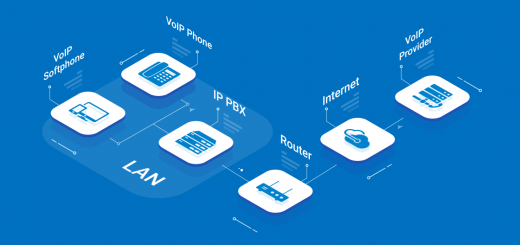
SIP and SIP Addresses
You may be confused about the difference between SIP and VoIP. (Evolving Internet technology is lovely, but it does come with a staggering number of acronyms.) VoIP is calling over the Internet, while SIP is the protocol behind VoIP. Short for Session Initiation Protocol, SIP’s full name pretty much explains its function just like Voice over IP does.
SIP is VoIP’s signaling protocol—it’s what allows the call to actually connect and disconnect. Beyond that, SIP enables you to change the basic functions of a VoIP call in real time, like adding people to a conference or having one person hang up while the others stay on the line.
If the term “protocol” is throwing you off, let us bring you into some familiar territory. We’re positive you know HTTP, and you know SMTP by function if not necessarily by name. These are common communication protocols as well. HTTP is for the World Wide Web; it’s how your browser and the website you’re on communicate and exchange data. Without HTTP, hyperlinks wouldn’t work. SMTP is the protocol behind email and is quite similar to SIP.
What Is a VoIP Number?
The terms “VoIP number” and “virtual phone number” are used fairly interchangeably in the digital telecom industry. Having a virtual phone number simply means that the number is not tied to a specific device. With landline phones, each number corresponds to a specific phone at a specific location. Cell phones function quite similarly—they might be mobile, but when you call your mother’s cell phone number, you know that call connects directly with her specific device. VoIP numbers, on the other hand, are associated with a particular individual rather than a device.
Think of your VoIP number like your email: As long as you have the credentials and an Internet-capable device, you can log in anywhere to send and receive messages. This geographic flexibility is what makes VoIP such an ideal business tool for employees who don’t stay at their desk all day.
What Is a VoIP Phone?
A VoIP phone looks just like a regular phone, but haven’t you ever heard you shouldn’t judge a book by its cover? VoIP phones ditch the landline wiring and bring in superior features and functionality. They often use Power over Ethernet (PoE), which means that an Ethernet cable plugged into the back of the unit both powers the device and connects it to the Internet. This is great for businesses because rather than having to get a whole office wired or adding lines for new hires, employees can just plug their phones in and hop on a call within minutes. Even better, once a phone is configured for VoIP you can take it anywhere, plug it back in, and it will work just the same.
VoIP for Business: The Benefits
Once you start talking about the benefits of business VoIP, it’s difficult to know where to end. At least it’s easy to figure out where to start:
Cost
The most significant benefit of switching your business to a cloud-based phone system is by and large the expense. Traditional phone systems are expensive when you consider hardware, provider fees, installation, and actual per-minute costs. VoIP phones can handle multiple “lines” at once, can be installed in no time, and don’t cost nearly as much because the technology harnesses the wonderfully free power of the Internet. VoIP is an excellent choice for businesses that don’t want to spend inordinate amounts of money on their phone bill.
Scalability
As businesses grow and add employees, adding additional VoIP lines is extraordinarily simple. A landline phone system would require calling your provider, setting up a time for them to add lines to the office, and buying new hardware. With cloud-based phone systems like OnSIP, you can control everything from our online admin portal. As your business grows, moves, or changes in any way, you can make necessary adjustments on your own.